.NET Framework
.NET Framework is a managed execution environment for Windows that allows software developers to create a software application in one programming language and be assured that the app will be able to work with code written in other languages. The framework, which is designed to accommodate object code no matter where it is stored or executed, is the primary implementation of Microsoft’s .NET technologies.
The .NET platform was designed to reduce programming errors and increase productivity by using a modular approach to software design. The framework features a common language runtime (CLR) and a class library. The CLR is Microsoft’s implementation of the common language infrastructure (CLI), a standard for helping different programming languages and libraries work together. The CLR manages system services such as memory, thread execution, code execution, code safety verification and compilation. The class library contains tested, reusable code that developers can call from their own apps to provide functionality for such things as file input/output, parsing Extensible Markup Language (XML) and working with Windows Forms.
Microsoft’s development tool for designing and developing .NET apps is called Visual Studio and apps are typically written in Visual Basic (VB) or C#. The Microsoft Test Framework (MSTest) can be used to provide quality assurance (QA) for .NET applications.
How the .NET Framework works
Source code written in one language is compiled into an intermediate language (IL) which is stored on disk in an executable file called an assembly. The assembly contains a manifest that provides information about the code’s type, version and security requirements. Once the assembly is loaded into the CLR and validated, the IL code can be translated into native machine code instructions.
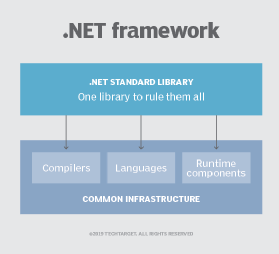
Language compilers for the .NET Framework use the Common Intermediate Language (CIL), an intermediate code that is compiled at runtime by the common language runtime. The .NET Framework helps resolve version conflicts because it allows multiple versions of the CLR to exist on the same computer.
Other .NET technologies
.NET Core is a cross-platform fork of .NET that allows developers to build apps that can run on Linux and Mac operating systems, as well as Windows. NET Core 3.0 is specifically designed for containerized microservices and cloud applications, can target Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) and Windows Forms, the two most commonly used frameworks for Windows desktop applications. NET Core is open source and can be downloaded from GitHub.
.NET Standard is a formal specification of the application program interfaces (APIs) that are common across .NET implementations. .Net Standard allows the same code and libraries to run on different implementations and expose additional APIs that are specific to the operating systems the implementation runs on.
ASP.NET features server controls that can separate code from the content to allow WYSIWYG editing.
.NET Micro Framework is a .NET platform for extremely resource-constrained devices in the Internet of Things (IoT).
ML.NET is an open-source, cross-platform machine learning (ML) framework for the .NET ecosystem.